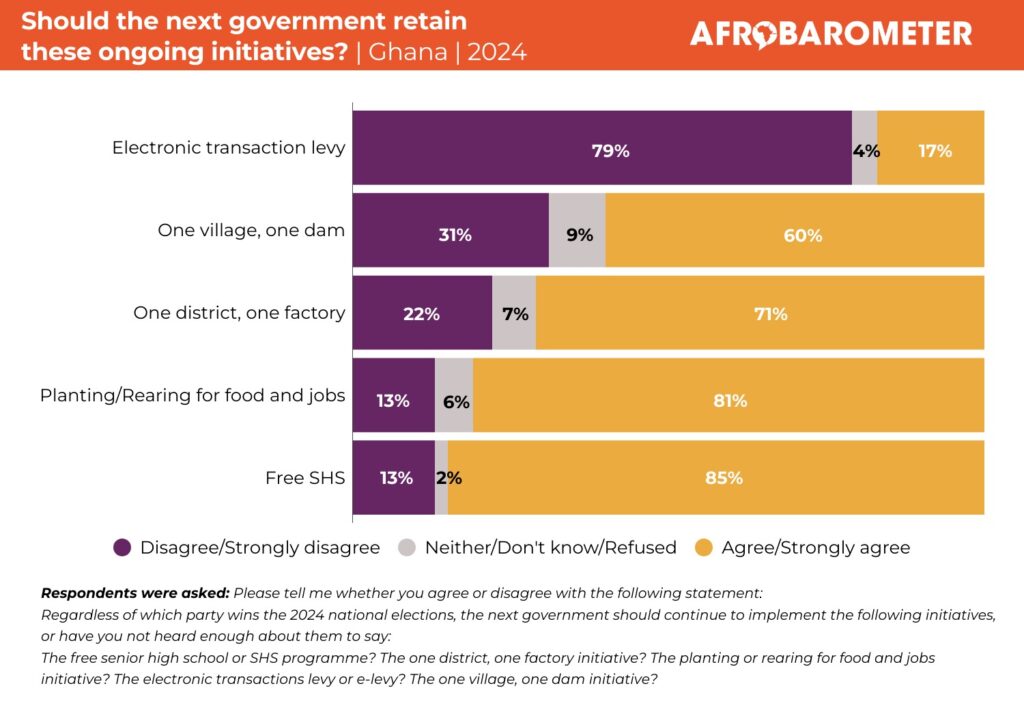
On September 29, 2023, Ghana’s President Akufo-Addo said this “As all of us know, despite the considerable progress made by the community, in the areas of democracy, good governance and the rule of law since the early 1990s, which meant that, four (4) years ago, all fifteen (15) leaders of ECOWAS States were democratically elected, we are, at the moment, witnessing a decline in our democratic credentials.”
Military takeovers in Mali, Guinea, Niger, Burkina Faso, and Gabon between 2020 and 2023 has been enough to raise alarms about the threats to democracy in the sub region. And when one factors in the region’s history with military coups before the third wave of democracy, the president’s worry is spot on.
President Akufo-Addo also said, “Democracy in West Africa is in danger.”
In the maiden edition of the Afrobarometer survey (1999-2001), three countries from West Africa participated. In the most recent survey round (2021-2023), fourteen countries from the region participated. The increased participation in the survey means that the signals are coming from more voices (from 7,694 to 19,568 respondents) across more countries in the region.
There is surely country variation in how citizens across the region feel about democracy. However, for the purpose of this piece, I am interested in examining the collective voice of West Africans.
So, what really is the situation in West Africa? What are these danger signs?
The Danger Signs
In survey period 1999-2001, eight out of ten (83%) citizens in the region disapproved of military rule. In survey period 2021-2023, six out of ten (63%) citizens in the region disapproved of military. Let’s look at it from another angle. From only thirteen percent (13%) approving of military rule in survey period 1999-2001, that increased to thirty-five percent (35%) in survey period 2021-2023.
And in the most recent survey period (2021-2023) when asked whether – a) armed forces should never intervene in the country’s political process or b) if it was legitimate for the armed forces to take control of government when elected leaders abuse power for their own ends” as many as six out of ten (56%) supported the legitimacy of military intervention.
So, as you can see, there has been what I call “a softening” in the attitudes of citizens in West Africa towards military rule.
When asked about the extent of democracy, in survey period 2002-2003, eight percent (8%) said “not a democracy,” but in survey period 2021-2023, sixteen percent (16%) said “not a democracy.” Over the same period, there has been no significant change in the percentage who said, “full democracy” (15% to 16%); or who said a) democracy with major problems (still at 37%); b) democracy with minor problems (33% to 30%). The doubling of the percentage of those saying “not a democracy” is a sign that there is growing doubts about the democratic credentials of countries in the region.
In survey period 1999-2001, seven out of ten (70%) West-Africans said they were satisfied with the way democracy was working. In survey period 2021-2023, that dropped sharply to four out of ten (36%). A sharp decrease in the level of satisfaction with the way democracy is working erodes the confidence of citizens. And that was very clear when citizens were asked in the same survey period about the level of democracy in five years. Only four out of ten (38%) felt the region will be more democratic.
These are some of the danger signs to democratic governance in the region.
Some Bright Spots
While we cannot ignore the danger signs, there are some bright spots that can be leveraged in the fight to halt democratic backsliding in the region. First, there is still strong preference for democracy among West- Africans. That support was seventy-four percent (74%) in survey period 1999-2001 and seventy percent (70%) in survey period 2021-2023.
Second, there is still strong preference for a key democratic activity – the use of elections as the key method for choosing leaders. In survey period 2002-2003, eighty-one percent (81%) expressed support for elections. In survey period 2021-2023, seventy-eight percent (78%) still expressed support for elections. To add, confidence in elections (the percentage of those who say the most recent election was completely free and fair) has improved. In survey period 1999-2002, twenty-seven percent (27%) had confidence in election outcomes compared to forty percent (40%) in survey period 2021-2023.
What Next?
I must note that this is the collective picture. The danger signs are more pronounced in some countries than others. This is not an attempt to treat the region as politically monolithic. We must however by mindful of the danger signs and do two things – a) find out the drivers of the danger signs; and b) actively take steps to diffuse and reverse them.
 John Osae-Kwapong (PhD) is a Democracy and Development (D&D) Fellow at CDD-Ghana, Associate Provost for Assessment, Accreditation, and Institutional Effectiveness, Baruch College, The City University of New York.
John Osae-Kwapong (PhD) is a Democracy and Development (D&D) Fellow at CDD-Ghana, Associate Provost for Assessment, Accreditation, and Institutional Effectiveness, Baruch College, The City University of New York.